Chapter 4
Cell Reproduction
Cell Division and Mitosis
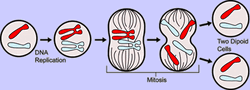
Courtesy of Windows to the Universe
In section one of chapter four, you learn about how cells divide. There are six stages in this process. Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis are the stages. In interphase, chromosomes duplicate, and the nucleus and nucleus are clearly visible inside the cell. Next comes prophase. Spindle fibers start to reach out across the cell towards the chromosomes, which are connected at the centromere. In the next stage, metaphase, the chromatid pairs line up around the center of the cell. In anaphase, the chromatid pairs separate. Then in telophase, the cell membrane begins to pinch in, and there are two nuclei. Finally in cytokinesis, the cytoplasm splits, and two identical daughter cells have formed.
Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis

Courtesy of Baby Animalz.com
This is the second section in chapter four. This lesson is about sexual reproduction, or when an organism is born by two parents. An egg is a sex cell formed in the female reproductive organs, and a sperm is formed in the male reproductive organs. When the chromosomes of the egg and sperm come together, which is called fertilization, a zygote forms. This is the beginning of a diploid organism, or an organism with similar chromosomes.
DNA
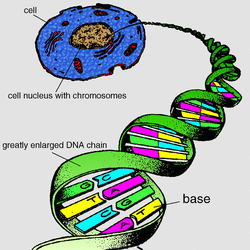
Courtesy of Cerebellar Ataxia Information
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is what makes up chromosomes. DNA makes us who we are. It is a chemical stored in hereditary material. DNA is like a twisted ladder. The two sides of the strand are made pf a sugar called deoxyribose, and the what would be the rungs of the ladder are nitrogen bases. There are four nitrogen bases on DNA. They are adenine, or A, guanine, which is G, cytosine, or C, and thymine, which is T. T only pairs with A, and C only pairs with G on DNA.
RNA is ribonucleic acid. RNA has the same nitrogen bases that DNA does, except T is U, or uracil. There are three types of RNA. The rRNA is ribosomal RNA, which makes up ribosomes. There is also tRNA and mRNA, which means transfer and messenger RNA. All of these types of RNA are important in the process of making proteins.
RNA is ribonucleic acid. RNA has the same nitrogen bases that DNA does, except T is U, or uracil. There are three types of RNA. The rRNA is ribosomal RNA, which makes up ribosomes. There is also tRNA and mRNA, which means transfer and messenger RNA. All of these types of RNA are important in the process of making proteins.
