Chapter 17
Structure and Movement
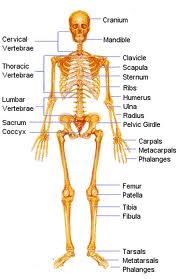
The Skeletal System
Courtesy of What the World is
Looking for Chiff.com Web Guide
There are five main functions of the skeletal system. They are:
1. Giving shape and support to your body.
2. Protecting your internal organs.
3. Major muscles are attached to bone and help them move.
4. Blood cells are formed in the center of many bones.
5. Much calcium and phosphorus is stored in the bones. Periosteum is a tight-fitting membrane that is the outer covering for the bones. Right under the periosteum is compact bone, which is hard and tough. The compact bone is actually living, because it is made of cells. Directly under the compact bone is spongy bone. Spongy bone has many holes in it, which makes it lightweight. A substance called marrow fills these holes. Marrow is either red or yellow: yellow is a fatty tissue, and red makes red blood cells.
Cartilage is a smooth, thick, slippery layer of tissue at the end of bones. Cartilage acts as a shock absorber for the bones. It is very important in this way.
Anyplace where two or more bones come together is called a joint. There are many different types of joints, such as pivot, ball-and-socket, and hinge, which are all movable joints. Immovable joints cannot move no matter what. An example of a fixed joint would be where the bones in a human's skull come together. Muscles move the bones they are connected to by moving joints.
A ligament holds bones together at joints. Ligaments are tough bands of tissue. Sometimes more than one ligament will hold the specific bones in place.
1. Giving shape and support to your body.
2. Protecting your internal organs.
3. Major muscles are attached to bone and help them move.
4. Blood cells are formed in the center of many bones.
5. Much calcium and phosphorus is stored in the bones. Periosteum is a tight-fitting membrane that is the outer covering for the bones. Right under the periosteum is compact bone, which is hard and tough. The compact bone is actually living, because it is made of cells. Directly under the compact bone is spongy bone. Spongy bone has many holes in it, which makes it lightweight. A substance called marrow fills these holes. Marrow is either red or yellow: yellow is a fatty tissue, and red makes red blood cells.
Cartilage is a smooth, thick, slippery layer of tissue at the end of bones. Cartilage acts as a shock absorber for the bones. It is very important in this way.
Anyplace where two or more bones come together is called a joint. There are many different types of joints, such as pivot, ball-and-socket, and hinge, which are all movable joints. Immovable joints cannot move no matter what. An example of a fixed joint would be where the bones in a human's skull come together. Muscles move the bones they are connected to by moving joints.
A ligament holds bones together at joints. Ligaments are tough bands of tissue. Sometimes more than one ligament will hold the specific bones in place.
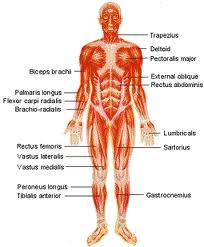
The Muscular System
Courtesy of What the World is Looking for
Chiff.com Web Guide
A muscle is an organ that can contract, relax, and provide the force to move your body parts. There are over 600 muscles in your body, but muscles always work in pairs. When one contracts, the other relaxes.
There are two types of muscles; voluntary and involuntary. Voluntary muscles are muscles that you can consciously control, but involuntary muscles cannot be controlled. Muscles like your heart and digestive tract cannot stop, and are moving constantly, but muscles in your arms and legs are controllable.
There are three classifications of muscle tissue. There is smooth, skeletal, and cardiac. Smooth and cardiac muscle tissues are in the heart and internal organs. They are both involuntary muscles. Skeletal muscle tissue is the muscles attached to your bones. These are the muscles that you can control, so they are called voluntary.
There are two types of muscles; voluntary and involuntary. Voluntary muscles are muscles that you can consciously control, but involuntary muscles cannot be controlled. Muscles like your heart and digestive tract cannot stop, and are moving constantly, but muscles in your arms and legs are controllable.
There are three classifications of muscle tissue. There is smooth, skeletal, and cardiac. Smooth and cardiac muscle tissues are in the heart and internal organs. They are both involuntary muscles. Skeletal muscle tissue is the muscles attached to your bones. These are the muscles that you can control, so they are called voluntary.
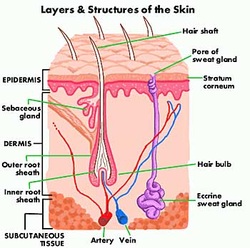
The Skin
Courtesy of Healthy-Skin-Guide.com
Though not everybody knows it, your skin is the largest organ in your body. Skin is made up of three layers- epidermis, dermis, and a fatty layer. The epidermis is the top layer. It is also the thinnest layer of the three. Below the epidermis is the dermis. It is thicker than the epidermis, and has many blood vessels, muscles, nerves, sweat glands, oil and other structures. Below this layer of skin is the fatty layer, which helps insulate the body. When somebody gains a lot of weight, this is where the fat goes.
Melanin is a pigment in your skin that determines how dark a person's skin is. When there is more melanin, the skin will look darker. Melanin is present in the epidermis of the skin.
The skin has five main functions. They are:
1. Protection
2. Sensory response
3. Formation of vitamin D
4. Regulation of body temperature
5. Ridding the body of wastes.
Protection is the skin's most important function. When you get a bruise or a cut, the skin does certain things to keep the body safe. A cut is any tear in the skin, and a bruise is when blood vessels beneath the skin burst.
Melanin is a pigment in your skin that determines how dark a person's skin is. When there is more melanin, the skin will look darker. Melanin is present in the epidermis of the skin.
The skin has five main functions. They are:
1. Protection
2. Sensory response
3. Formation of vitamin D
4. Regulation of body temperature
5. Ridding the body of wastes.
Protection is the skin's most important function. When you get a bruise or a cut, the skin does certain things to keep the body safe. A cut is any tear in the skin, and a bruise is when blood vessels beneath the skin burst.
